Physical Description
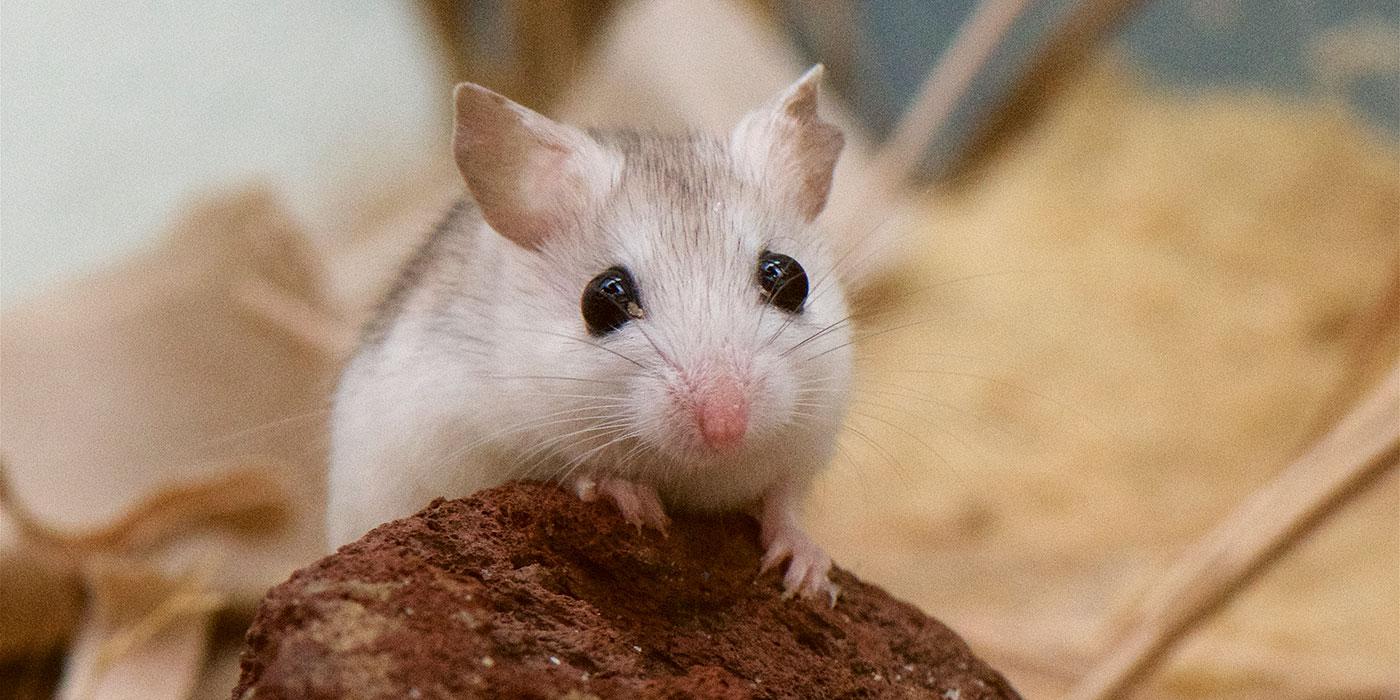
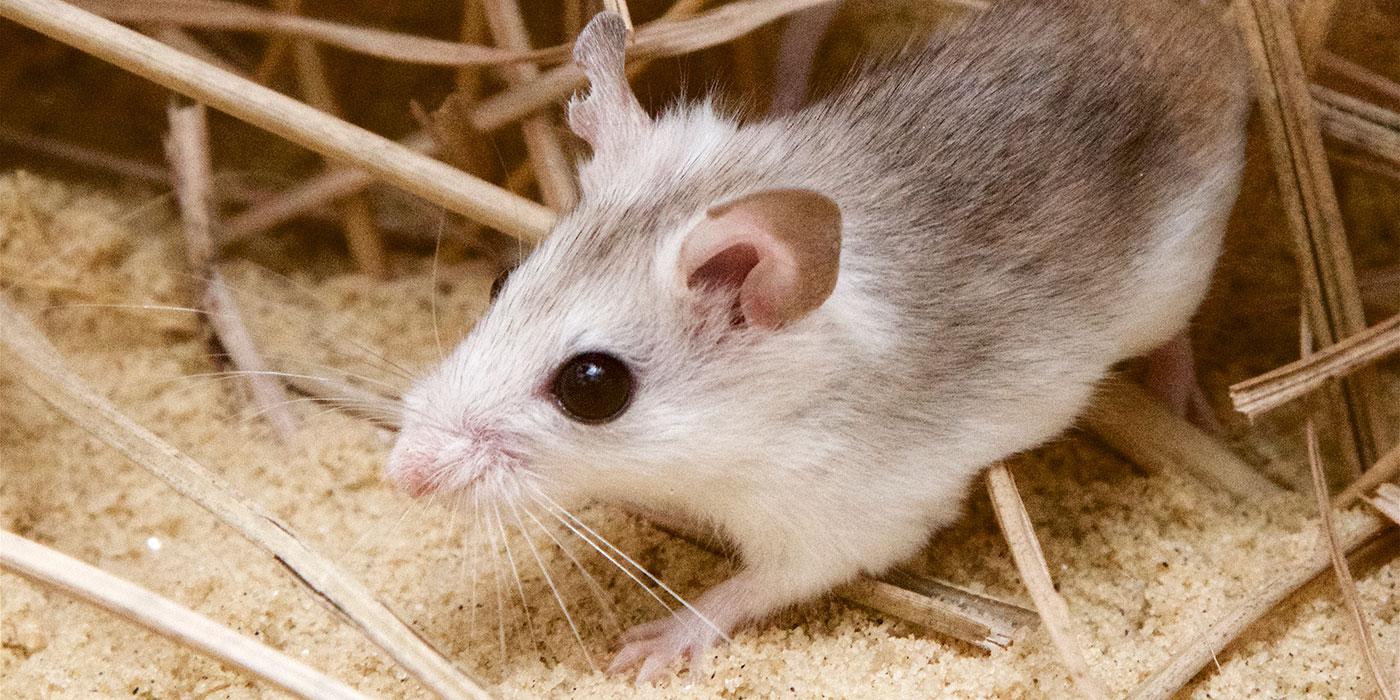
There are eight subspecies of beach mice, five of which live along the Gulf Coast. Perdido Key beach mice have small bodies, hairy tails, large ears and big eyes. Their bodies are grayish fawn to wood brown with a very pale-yellow hue.
Size
These mice are 2.7 to 3.3 inches long, excluding the tail. Their tails measure 1.7 to 2.5 inches. They weigh 13 grams.
Native Habitat
Beach mice inhabit frontal and scrub dunes along the coast of Florida and Alabama. They typically live in sparsely vegetated dunes just above the high-tide line and more densely vegetated dunes farther inland. These mice often maintain multiple burrows within a home range that averages 5,000 square meters. They use their burrows for sleeping, nesting, feeding, caching seeds and escaping from predators.
Lifespan
Perdido Key beach mice typically live for nine months to a year. They can live up to six years in human care.
Food/Eating Habits
Beach mice emerge from their burrows at night to forage on the seeds and fruits of beach plants, as well as on insects. Sea oats make up a large part of their diet, but they also feed on other seasonally available dune plant seeds, such as bluestem, ground cherry, evening primrose, beach pea and dune spurge.
Throughout the night, the mice make several trips to and from their burrows gathering seeds to store. At the Smithsonian's National Zoo, beach mice eat rodent chow and seeds. They also receive fruit and mealworms as enrichment.
Sleep Habits
Perdido Key beach mice are primarily nocturnal, spending the daylight hours in burrows.
Reproduction and Development
Beach mice are monogamous and pair for life, which is unusual among mammals of which only about 3 percent are monogamous. Breeding peaks during the winter months but can occur throughout the year if food is readily available.
Gestation totals 23 days, and the female gives birth to up to four pups per litter. Females are capable of breeding again as soon as 24 hours after giving birth. Offspring are weaned 18 days after birth and reach sexual maturity around 30 days old.
Conservation Efforts
Perdido Key beach mice are protected as an endangered species by the Endangered Species Act and as a federally designated endangered species by Florida's Endangered and Threatened Species Rule.
All subspecies of beach mice, with the exception of the Santa Rosa beach mouse, are state and federally protected.
Beach mice have specific habitat needs, which are threatened by human development that destroys dune habitat and limits food resources. Their populations are also at risk from introduced predators, such as domestic cats and red foxes.
The Smithsonian's National Zoo is the first zoo outside of Florida to house this species. Much like the black-footed ferret program, zoos assist U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service by housing and breeding these animals for reintroduction. As the program grows, retired breeders are also used for education and as ambassador animals.
Conserving beach mouse habitat helps sea turtles, shorebirds and other coastal species.
Help this Species
- Be a responsible cat owner, and keep cats indoors or under restraint when outside. Never release animals that have been kept as pets into the wild.
- Support organizations like the Smithsonian’s National Zoo and Conservation Biology Institute that research better ways to protect and care for this animal and other endangered species. Consider donating your time, money or goods.
- Share the story of this animal with others. Simply raising awareness about this species can contribute to its overall protection.